Introduction
In most homes, there are a wide variety of receptacle types. Each type serves a very specific purpose. In this section, you'll learn about choosing the right receptacle for any service upgrades or new circuits you may be planning.
|
Basic Receptacle Types
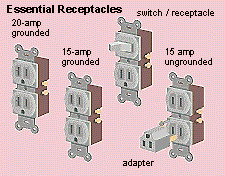
A standard duplex receptacle has two outlets for receiving plugs. Each outlet has a long (neutral) slot, a shorter (hot) slot, and a half-round grounding hole. This ensures that the plug will be polarized and grounded (see Grounding and Polarization, Related Projects). Receptacles are rated for maximum amps.
A 20-amp grounded receptacle has a T-shaped neutral slot; use it only on 20-amp circuits.
|
|
The switch in a combination switch/receptacle can be hooked up to control the receptacle it's paired with.
|
Special Purpose Receptacles
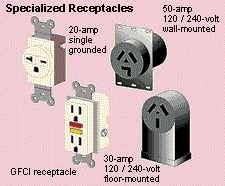
A standard duplex receptacle has two outlets for receiving plugs. Each outlet has a long (neutral) slot, a shorter (hot) slot, and a half-round grounding hole. This ensures that the plug will be polarized and grounded (see Grounding and Polarization, Related Projects). Receptacles are rated for maximum amps.
A 20-amp grounded receptacle has a T-shaped neutral slot; use it only on 20-amp circuits.
|
|
The switch in a combination switch/receptacle can be hooked up to control the receptacle it's paired with.